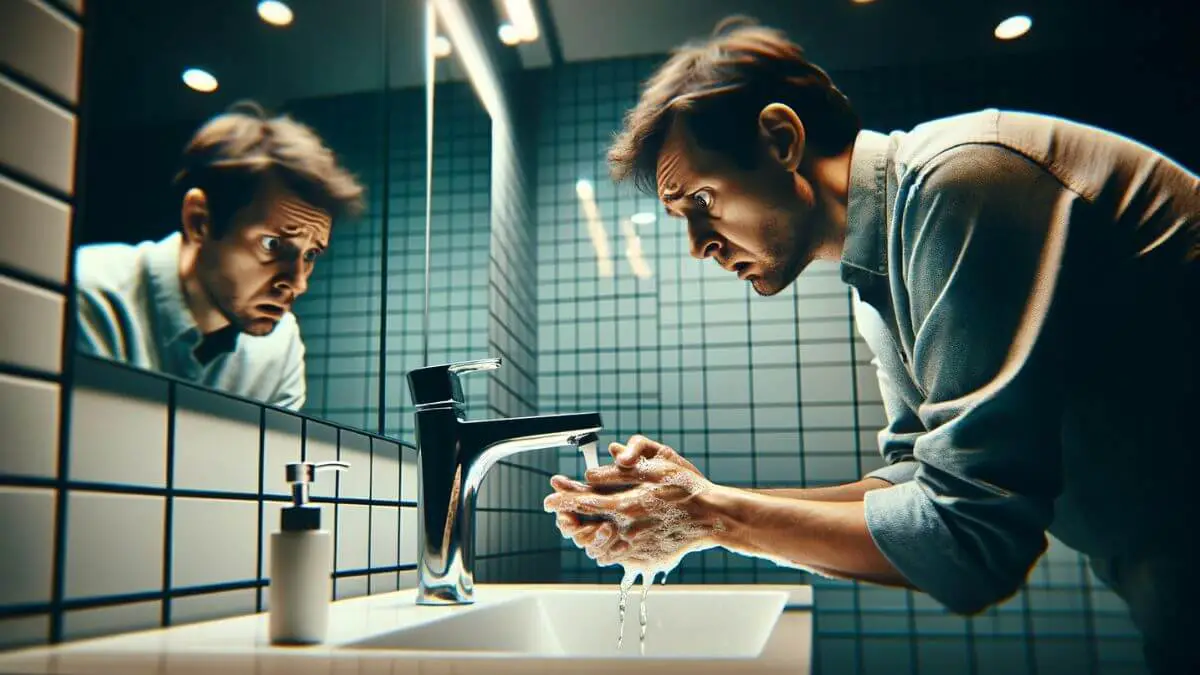
Understanding OCD in Chronic Illness
Understanding OCD in chronic illness is hard, not to say impossible, if you don’t suffer from either yourself. You see, I’m a bloke who is healthy, but my wife suffers from endometriosis and fibromyalgia, but also general anxiety, OCD, and depression.
Even though I observe her daily, I will never be able to fully grasp what she’s going through. I am not in her body. Period. But I do know this much:
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, is a mental health condition characterized by persistent intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions). People with chronic illnesses may experience heightened levels of OCD due to the stress and uncertainty associated with their health conditions.
Understanding OCD in the context of chronic illness is essential for providing effective mental health support and improving overall well-being.
Let’s dive into the details. Scroll down to learn more about OCD and chronic illness…
- Understanding OCD in Chronic Illness
- The Prevalence of Chronic OCD
- Understanding OCD Symptoms in Chronic Illness
- Managing OCD in the Context of Chronic Illness
- Impact of OCD on Chronic Illness
- Treatment Options for OCD in Chronic Illness
- Strategies for Coping with OCD and Chronic Illness
- Understanding the Connection Between OCD and Chronic Illness
- Education and Awareness for OCD and Chronic Illness
- Research and Advances in OCD and Chronic Illness
- Seeking Help for OCD in Chronic Illness
- Conclusion on Understanding OCD in Chronic Illness
- Source Links for Understanding OCD in Chronic Illness
Understanding OCD in Chronic Illness
If you or someone you know is living with both obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and a chronic illness, it is important to gain a deeper understanding of how these conditions intersect and impact each other.
OCD is a mental health disorder characterized by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) that are intended to alleviate anxiety. Chronic illness, on the other hand, refers to a long-term medical condition that requires ongoing management and treatment.
Living with OCD and chronic illness can pose unique challenges, as both conditions can significantly impact daily life, well-being, and overall quality of life. It is crucial to recognize and address the symptoms of OCD within the context of chronic illness in order to effectively manage both conditions.
In this article, we will delve into the symptoms of OCD in the context of chronic illness, explore strategies for managing OCD in the presence of a chronic illness, discuss the impact of OCD on chronic illness, and highlight treatment options and resources available for individuals living with both conditions.
If you want more in-depth information about how to support your partner with her chronic conditions and how to cope with the new normal in your relationship, I wrote a “Supporting a Chronically Ill Partner” e-Book.
You can get the 1st Chapter of the e-Book for FREE, and if you like it, you’ll get a Whopping 33% Discount on the Whole Book, plus discounts on other helpful tools. You have nothing to lose but a lot to gain!
The first chapter alone contains a lot of information for both of you about acknowledging the struggles, including:
- A word to your partner.
- A word to you.
- Stepping on eggshells.
- Understanding her needs.
- How to acknowledge having a chronically ill partner?
- Acknowledging can be hard.
- 15 tips on how to do it!
Get the 1st Chapter FREE!
Chronic Illness for Partners

The Prevalence of Chronic OCD
Chronic OCD, characterized by persistent and long-lasting symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder, is a common occurrence among individuals with OCD. A study conducted by the Netherlands Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Association (NOCDA) shed light on the prevalence and impact of chronic OCD in individuals with chronic illness.
The study revealed that 61.7% of participants reported a chronic course of OCD, indicating the long-term nature of this condition. Chronic OCD was found to be associated with more severe OCD symptoms, higher illness burden, and greater comorbidity with other mental health conditions. Individuals experiencing chronic OCD also reported an earlier onset of OCD symptoms, suggesting the persistence of the disorder over time.
Specific Symptoms in Chronic OCD
Chronic OCD was found to manifest in various ways, with specific symptoms playing a significant role in its identification and diagnosis. The study highlighted that individuals with chronic OCD commonly experience contamination and washing symptoms, characterized by an excessive fear of germs and a compulsive need for cleanliness. Additionally, symmetry and ordering symptoms were also prevalent, wherein individuals feel the need for things to be in a particular order or arrangement.
| Prevalent Symptoms in Chronic OCD: | Percentage of Participants |
|---|---|
| Contamination and washing symptoms | 76.5% |
| Symmetry and ordering symptoms | 65.2% |
The Burden of Chronic OCD
The presence of chronic OCD in individuals with chronic illness can significantly impact their overall well-being and quality of life. The study found that chronic OCD was associated with a higher illness burden, indicating the increased distress and impairment caused by the condition. The chronicity of OCD also exacerbates the challenges faced by individuals with chronic illness, further complicating their management and treatment approaches.
Understanding the prevalence and specific symptoms of chronic OCD in individuals with chronic illness highlights the need for improved understanding, accurate diagnosis, and targeted treatment strategies for this population. By addressing the chronicity of OCD and its associated symptoms, healthcare professionals can better support individuals in managing their OCD symptoms alongside their chronic illness.

Understanding OCD Symptoms in Chronic Illness
Living with both OCD and chronic illness can result in a range of symptoms that significantly impact your daily life and functioning. It’s important to understand these symptoms and their impact in order to effectively manage and treat OCD in the context of chronic illness.
OCD symptoms in the context of chronic illness can include intrusive thoughts and anxiety. Intrusive thoughts are repetitive and unwanted thoughts that can be distressing and cause significant anxiety. These thoughts may revolve around safety, cleanliness, or harm, and can be difficult to control or dismiss.
Additionally, individuals with OCD and chronic illness may experience obsessions and compulsions. Obsessions are persistent and unwanted thoughts, images, or impulses that intrude upon your mind and cause distress. These obsessions can be related to your chronic illness, such as fears of contamination or intrusive thoughts about your health.
Compulsions, on the other hand, are repetitive behaviors or mental acts that you feel compelled to perform in response to obsessions. These compulsions are often done as a way to reduce anxiety or prevent a feared outcome. Common examples of compulsions include repetitive hand washing, excessive checking, or performing rituals or specific routines.
Impact on Daily Life
The impact of OCD symptoms in chronic illness can be significant. These symptoms can consume your thoughts, time, and energy, making it challenging to focus on daily tasks or engage in meaningful activities. OCD symptoms can interfere with work, relationships, and overall quality of life.
The constant presence of intrusive thoughts and the need to perform compulsions can be exhausting and distressing. They can lead to heightened levels of anxiety, stress, and isolation, making it difficult to manage the demands of chronic illness effectively.
Individuals with OCD and chronic illness may find themselves caught in a cycle of obsessions and compulsions that can be difficult to break. This can further exacerbate the challenges of living with a chronic illness, as the symptoms of OCD may perpetuate stress and anxiety, which can negatively impact overall well-being.
It’s important to recognize that OCD symptoms in the context of chronic illness are treatable, and effective management strategies are available to help you regain control and improve your quality of life.
Understanding the specific OCD symptoms you experience in the context of your chronic illness is crucial for effective management and treatment. By working with healthcare professionals experienced in both OCD and chronic illness, you can develop personalized coping strategies and interventions that address your unique needs and challenges.
| OCD Symptoms | Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|
| Intrusive Thoughts | Can cause significant anxiety and distress, making it challenging to focus on daily tasks |
| Obsessions | Can intrude upon your mind, leading to heightened levels of anxiety, stress, and isolation |
| Compulsions | Consumes time and energy, interferes with work and relationships, and can perpetuate stress and anxiety |
Managing OCD in the Context of Chronic Illness
Managing obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in the context of chronic illness requires a comprehensive approach. Individuals living with both OCD and chronic illness can benefit from a combination of coping strategies, therapy, medication, and support.
1. Coping Strategies
Developing effective coping strategies is essential for managing OCD symptoms in the face of chronic illness. Consider incorporating the following techniques:
- Relaxation Techniques: Engage in activities like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
- Self-Care Practices: Prioritize self-care activities such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, getting enough sleep, and engaging in pleasurable activities.
- Stress Reduction: Identify and implement stress reduction techniques that work best for you, such as mindfulness, journaling, or spending time in nature.
2. Therapy
Therapy is a vital component of managing OCD in the context of chronic illness. Two effective therapeutic approaches for OCD include:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies to manage OCD symptoms.
- Exposure and Response Prevention Therapy (ERP): ERP involves gradually exposing individuals to their obsessions and preventing the accompanying compulsions. This helps reduce anxiety and break the cycle of OCD behaviors.
3. Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage OCD symptoms. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly used to treat OCD and can be beneficial in reducing obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the right medication and dosage for your specific needs.
4. Support
Building a strong support network and accessing appropriate resources can provide invaluable assistance in managing OCD and chronic illness. Consider the following sources of support:
- Professional Support: Seek guidance from healthcare professionals experienced in treating OCD and chronic illness. They can provide personalized advice, treatment options, and necessary referrals.
- Support Groups: Join local or online support groups specific to OCD and chronic illness. Connecting with others who understand your experiences can offer validation, encouragement, and practical tips for managing symptoms.
- Family and Friends: Reach out to loved ones for emotional support and understanding. Educating them about OCD and chronic illness can help foster empathy and strengthen your support system.
Understanding OCD in Chronic Illness Table 3
Impact of OCD on Chronic Illness
The presence of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in individuals with chronic illness can have a profound impact on their overall quality of life. OCD is a chronic mental health condition characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors that can significantly interfere with daily activities and relationships. When coupled with the challenges of chronic illness, the impact of OCD becomes even more pronounced.
OCD symptoms, such as obsessive thoughts and compulsive rituals, can consume a significant amount of time and energy, making it difficult for individuals to manage their chronic illness effectively. These symptoms can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and decreased ability to adhere to treatment and self-care regimens.
Moreover, the relentless nature of OCD can exacerbate the physical symptoms and emotional distress associated with chronic illness, further compromising the individual’s well-being. This can result in reduced quality of life, limited participation in social activities, and increased dependence on healthcare services.
Research has shown that individuals with both OCD and chronic illness may have higher rates of healthcare utilization compared to those without OCD. The compounding effects of these two conditions can lead to increased healthcare costs and resource utilization.
Recognizing and addressing the impact of OCD on chronic illness is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and overall well-being. By identifying and managing OCD symptoms effectively, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with and manage their chronic illness, leading to a better quality of life.
The Impact of OCD on Daily Life
The impact of OCD on daily life in individuals with chronic illness is far-reaching, affecting various aspects of their well-being and functioning:
- Interference with daily activities: OCD symptoms can consume a significant amount of time and energy, making it difficult for individuals to engage in essential activities related to their chronic illness management, such as medication adherence, therapy sessions, and self-care routines.
- Strained relationships: The obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors associated with OCD can strain relationships with family, friends, and healthcare providers. This can result in social isolation, reduced support, and increased feelings of distress.
- Reduced treatment adherence: OCD symptoms can interfere with an individual’s ability to adhere to their chronic illness treatment plan. This may include missing medication doses, neglecting medical appointments, or disregarding self-care recommendations.
Addressing the impact of OCD on chronic illness requires a comprehensive approach that integrates effective treatment strategies for both conditions. Through therapy, medication, and support systems, individuals can develop coping mechanisms and strategies to better manage their OCD symptoms, improve treatment adherence, and enhance their overall well-being.
| Impact of OCD on Chronic Illness | Strategies for Improvement |
|---|---|
| Reduced quality of life | Utilize cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure and response prevention therapy (ERP) to address OCD symptoms and improve overall well-being. |
| Impaired treatment adherence | Implement reminders, organizational strategies, and support systems to enhance treatment adherence, such as medication management apps, therapy sessions, and peer support groups. |
| Increased healthcare utilization | Develop integrated healthcare plans that address both OCD and chronic illness, including specialized mental health support and comprehensive care coordination. |
Strategies for Improvement
Recognizing the impact of OCD on chronic illness is the first step towards improvement. Here are some strategies that can help individuals better manage the impact of OCD on their daily lives and chronic illness:
- Therapy: Engage in evidence-based therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure and response prevention therapy (ERP) to effectively manage OCD symptoms and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
- Medication: Consult with a healthcare provider to explore medication options that can alleviate OCD symptoms and improve overall well-being in the context of chronic illness.
- Support systems: Build a strong support network consisting of family, friends, and support groups to provide emotional support, encouragement, and understanding throughout the challenges of managing both conditions.
By implementing these strategies and seeking appropriate support, individuals with both OCD and chronic illness can mitigate the impact of OCD on their overall quality of life, enhance treatment adherence, and improve their ability to manage their chronic illness effectively.
Treatment Options for OCD in Chronic Illness
When it comes to managing OCD in the context of chronic illness, there are several treatment options available. These options typically involve a combination of medication, therapy, and self-help strategies that can help individuals effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Medication
One common treatment approach for OCD is the use of medication, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). These medications can help regulate the levels of serotonin in the brain, reducing the intensity of OCD symptoms. SSRIs are often prescribed alongside therapy to provide comprehensive treatment.
Therapy
Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure and response prevention therapy (ERP), is another crucial treatment option for OCD. CBT helps individuals identify and challenge their obsessive thoughts and learn healthier ways to cope with anxiety, while ERP focuses on gradually exposing individuals to situations that trigger their obsessions and guiding them in refraining from engaging in compulsive behaviors.
Self-Help Strategies
In addition to medication and therapy, self-help strategies can play a significant role in managing OCD in the context of chronic illness. These strategies may include practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and utilizing support networks. Self-help strategies empower individuals to take an active role in their treatment and provide valuable tools for managing symptoms on a day-to-day basis.
Strategies for Coping with OCD and Chronic Illness
Coping with OCD and chronic illness can be challenging, but there are effective strategies you can implement to manage your symptoms and improve your well-being. The key is to prioritize self-care, practice stress management techniques, and build a strong support system.
Self-Care Practices
- Engage in regular exercise to promote physical and mental health.
- Implement relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, to reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm.
- Maintain a balanced lifestyle by prioritizing activities that bring you joy and fulfillment.
Stress Management Techniques
- Identify your stress triggers and develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage them effectively.
- Practice time management strategies to reduce overwhelm and create a sense of control.
- Consider seeking professional help from therapists or counselors specializing in stress management.
Building a Support System
- Reach out to family and friends who can provide emotional support and understanding.
- Join support groups or online communities dedicated to individuals coping with OCD and chronic illness.
- Consider therapy or counseling to work through your emotions and challenges in a safe and supportive environment.
Remember, coping with OCD and chronic illness is a journey, and it’s important to be patient and kind to yourself along the way. By implementing these strategies and accessing the appropriate support, you can effectively manage your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
Understanding the Connection Between OCD and Chronic Illness
The connection between OCD and chronic illness is complex, with shared underlying factors potentially influencing the development and course of both conditions.
Individuals living with chronic illness may experience an exacerbation of OCD symptoms, which can further impact their overall well-being and quality of life. The presence of OCD can contribute to increased distress and impaired functioning in individuals with chronic illness, creating additional challenges to manage.
By understanding the relationship between OCD and chronic illness, healthcare providers can provide comprehensive care and support that addresses the unique needs of individuals dealing with both conditions. It is crucial to recognize the impact of each condition on the other and implement strategies for effective management.
Supporting individuals with OCD and chronic illness involves addressing the shared underlying factors and tailoring treatment plans to address the specific needs of each individual. By recognizing and addressing these connections, healthcare providers can work towards improving outcomes and helping individuals lead fulfilling lives.
The Impact of Shared Underlying Factors
The relationship between OCD and chronic illness can be attributed to shared underlying factors, such as genetic predisposition, neurobiological mechanisms, and psychological vulnerabilities. These factors can influence the development and course of both conditions, creating a complex interplay between OCD and chronic illness.
Managing OCD and Chronic Illness Together
Managing OCD in the context of chronic illness requires a comprehensive approach that considers the unique challenges posed by both conditions. It is important to develop individualized treatment plans that incorporate therapy, medication, self-help strategies, and support systems.
| OCD in Chronic Illness | Chronic Illness in OCD |
|---|---|
| Increased symptom severity | Impaired functioning |
| Elevated distress | Greater illness burden |
| Compromised quality of life | Interference with daily activities |
| Higher healthcare utilization | Impact on treatment adherence |
Providing Comprehensive Care and Support
To provide comprehensive care and support for individuals dealing with both OCD and chronic illness, healthcare providers must collaborate across disciplines and consider the unique needs of each individual. By understanding the connections, implementing tailored treatment approaches, and fostering a supportive environment, individuals can better manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Next, we will explore the importance of education and awareness for OCD and chronic illness, and how it can contribute to reducing stigma and promoting a better understanding of these conditions.
Education and Awareness for OCD and Chronic Illness
Educating individuals and raising awareness about OCD in the context of chronic illness is crucial in combating stigma and promoting understanding.
By increasing knowledge about the challenges faced by individuals living with both conditions, we can foster empathy and support, ultimately improving the lives of those affected. Additionally, advocacy efforts play a vital role in advocating for access to appropriate resources and treatment options for individuals navigating the complexities of OCD and chronic illness.

The Impact of Education and Awareness
Education and awareness initiatives help break down the barriers and misconceptions surrounding OCD in the context of chronic illness. By dispelling myths and providing accurate information, we can reduce stigma and promote a more compassionate and inclusive society that supports individuals living with these conditions.
Increased awareness can also lead to early identification and intervention, ensuring individuals receive the necessary support and resources they need to manage their OCD symptoms alongside their chronic illness. This proactive approach can improve overall quality of life and enhance treatment outcomes.
Advocacy for Access and Support
Advocacy efforts are essential in promoting access to appropriate resources and treatment options for individuals living with both OCD and chronic illness. By advocating for policies and services that address the unique needs of this population, we can ensure that individuals receive the comprehensive care they require.
Advocacy can also help remove barriers to receiving treatment, such as insurance coverage or limited availability of specialized care. By advocating for increased funding and support, we can improve the accessibility and affordability of services for individuals navigating both OCD and chronic illness.
Together, education, awareness, and advocacy efforts can make a significant difference in the lives of individuals with OCD and chronic illness. By promoting understanding, providing support, and advocating for change, we can create a more inclusive and compassionate society that recognizes and addresses the unique challenges faced by those living with these conditions.
Research and Advances in OCD and Chronic Illness
Ongoing research and advancements in the field of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and chronic illness offer promising prospects for improved treatment options and interventions. As scientists and medical professionals continue to explore the relationship between these conditions, new insights are being gained, leading to enhanced quality of life for individuals living with both OCD and chronic illness.
The research focuses on identifying the underlying mechanisms and shared factors that contribute to the development and persistence of OCD in the context of chronic illness. By understanding these intricate relationships, researchers can develop targeted therapies and interventions that specifically address the unique challenges faced by individuals with both conditions.
Studies have shown that individuals with chronic illness who also experience OCD symptoms may benefit from a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. This approach involves combining medication, therapy, and self-help strategies to manage and alleviate symptoms effectively.
Targeted Therapies
One significant advancement in the treatment of OCD and chronic illness is the development of targeted therapies that address the specific needs of these individuals. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), in particular, has shown promising results in helping individuals manage their OCD symptoms while navigating the complexities of chronic illness.
Exposure and response prevention therapy (ERP) is another type of treatment that has proven effective for individuals with OCD. This therapy involves gradually exposing individuals to their fears or obsessions and preventing the associated compulsive response, helping to reduce anxiety and interrupt the cycle of OCD behaviors.
Pharmacological Interventions
Advancements in pharmacological interventions have also contributed to the improved management of OCD in the context of chronic illness. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed medications that help regulate serotonin levels in the brain, reducing the severity of OCD symptoms.
Although medication cannot cure OCD, it can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve overall functioning. Medical professionals carefully consider the individual’s specific circumstances and potential interactions with other medications before determining the most suitable pharmacological intervention.
Integration of Self-Help Strategies
Self-help strategies play a crucial role in the management of OCD and chronic illness. These strategies empower individuals to take an active role in their care and well-being. Practices such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, stress management, and self-care activities can complement therapy and medication, providing additional support and coping mechanisms for individuals living with both conditions.
In conclusion, ongoing research and advancements in the field of OCD and chronic illness hold great promise for individuals facing the challenges of both conditions. With the development of targeted therapies, the availability of pharmacological interventions, and the integration of self-help strategies, individuals can now access a comprehensive range of treatment options and interventions. By staying informed about the latest research and advancements, individuals, healthcare professionals, and support networks can continue to improve the lives of those living with OCD and chronic illness.
Seeking Help for OCD in Chronic Illness
If you or someone you know is living with both OCD and chronic illness, it is crucial to seek help from healthcare providers who specialize in treating these conditions. These professionals have the expertise and experience needed to provide guidance, resources, and appropriate treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Healthcare providers knowledgeable in OCD and chronic illness can assist in developing effective strategies to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. They can work with you to understand the unique challenges posed by both conditions and create a personalized treatment plan.
To find healthcare providers experienced in treating OCD and chronic illness, consider:
- Consulting with your primary care physician for referrals to specialists who can address both your chronic illness and OCD.
- Seeking recommendations from support organizations that focus on OCD and chronic illness. These organizations often have lists of healthcare providers who have specific expertise in these areas.
- Utilizing online resources and directories that allow you to search for healthcare professionals specializing in OCD and chronic illness in your area.
In addition to seeking help from healthcare providers, support resources such as organizations and online communities can be instrumental in navigating the challenges of living with both OCD and chronic illness. These resources offer valuable support, information, and a sense of community where individuals can connect with others who share similar experiences.
Remember, you don’t have to face OCD and chronic illness alone. Seeking help and utilizing available support resources can make a significant difference in managing your condition and improving your quality of life.
Conclusion on Understanding OCD in Chronic Illness
Understanding the complex relationship between OCD and chronic illness is essential for effective management and improved quality of life. Living with both conditions can present unique challenges, but by recognizing the impact of OCD on chronic illness and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can navigate these challenges more effectively.
Managing OCD in the context of chronic illness requires a comprehensive approach. This can involve utilizing coping strategies, such as relaxation techniques and stress reduction, therapy options like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure and response prevention therapy (ERP), and in some cases, medication. Building a strong support network and accessing appropriate resources can further aid in managing both OCD and chronic illness.
It is important to recognize that the presence of OCD in individuals with chronic illness can have a significant impact on their overall quality of life. Addressing the impact of OCD on chronic illness is essential for improving outcomes and overall well-being. By seeking help from healthcare providers and utilizing available support resources, individuals can gain guidance, resources, and appropriate treatment options to effectively manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.

About Me
Hi, I’m Lucjan! The reason why I decided to create this blog was my beautiful wife, who experienced a lot of pain in life, but also the lack of information about endometriosis and fibromyalgia for men…
